Cordycep Militaris - Inhibitory effects of bioactive extracts of Bacillus sp. H8-1 and Bacillus sp. K203 michiganensis in tomato wilting by Clavibacter michiganensis subsp.
Open Access Policy Institutional Open Access Program Special Issue Guidelines Editorial Process Research and Publication Ethics Article Processing Fees Winner Testimonials
Cordycep Militaris
All articles published by will be readily available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required when reusing all or part of a published article, including charts. For articles published under the open access Creative Commons CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission, as long as the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please visit https:///openaccess.
Transcriptome Wide Analysis Reveals The Progress Of Cordyceps Militaris Subculture Degeneration
Feature papers represent cutting-edge research with great potential for significant impact in this field. Feature papers are submitted by scientific editors at their personal invitation or recommendation and must be peer-reviewed before publication.
Feature papers are either original research articles, often fairly novel research studies involving multiple methods and approaches, or comprehensive review papers containing concise and precise updates on the latest advances in the field. science field. literature. Papers of this type provide insight into future research directions and potential applications.
Editor's Choice articles are based on recommendations by scientific editors of journals around the world. The editors select a small number of recently published articles in journals that they believe are of particular interest to readers or of importance in related research areas. The purpose of this journal is to provide a snapshot of the most exciting research published in various research fields.
Received: December 20, 2021 / Revised: February 3, 2022 / Accepted: February 8, 2022 / Published: February 10, 2022
Proceso De Establecimiento De Cordyceps Militaris En Botella De Vidrios Imagen De Archivo
Cordyceps (C. militaris) is a medicinal mushroom with diverse biological functions. It contains many biologically important components such as polysaccharides. The diverse medicinal potential of C. militaris has attracted interest in reviewing the current scientific literature, with a particular focus on the molecular mechanisms involved in prevention and inflammatory diseases. C. Military research has increased in recent years due to increasing global demand. c. militaryis has shown potential to suppress inflammation-related events in both in vivo and in vitro experiments. Inflammation is a multifaceted biological process that contributes to the development and severity of diseases such as cancer, colitis, and allergy. These actions make C. militaris a suitable functional food for inhibiting inflammatory responses, such as regulating pro-inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, based on existing information, the present study provides insight into the understanding of mechanisms associated with anti-inflammatory activity. This article presents the basis for clinical use and analyzes a roadmap for future research on the medical use of C. militaris and its next generation of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Inflammation is a complex process that occurs as a result of various chemical or physical agents in the body, including pathogens, trauma, and toxins [1]. The type of inflammatory stimulus and the efficacy of the response determine whether inflammation is acute or chronic in nature. Increased synthesis of inflammatory mediators is associated with chronic diseases such as cancer, arthritis, asthma, viral diseases, and atherosclerosis [2]. As a result, reducing inflammatory events has become important, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used for this purpose. NSAIDs have many side effects, including renal failure, bronchospasm, gastrointestinal disturbances, water retention, and hypersensitivity reactions [3].
As a result, considerable attention has recently been paid to developing natural anti-inflammatory products that are safe and have minimal side effects. Natural products have been used continuously since prehistoric times for the eradication of disease and overall well-being.The modern medical system began with the isolation of the pharmacologically active morphine. Morphine was the basis for the creation of a therapeutic empire composed of compounds isolated or derived from natural sources. Previously, a paradigm shift from isolation from natural sources to synthetic or combinatorial chemistry has led scientists to focus on large-scale synthesis of pharmaceuticals. Intensive efforts and declining productivity in synthetic processes have revived the involvement of natural products in drug development in recent decades, combined with new technological approaches such as high-throughput selection [4,5]. The conventional acceptance, cost-effectiveness, and unique chemical versatility of metabolites have led to the exploitation of natural resources for the identification of various pharmaceutical leads and scaffolds, serving the interests of mankind [6].
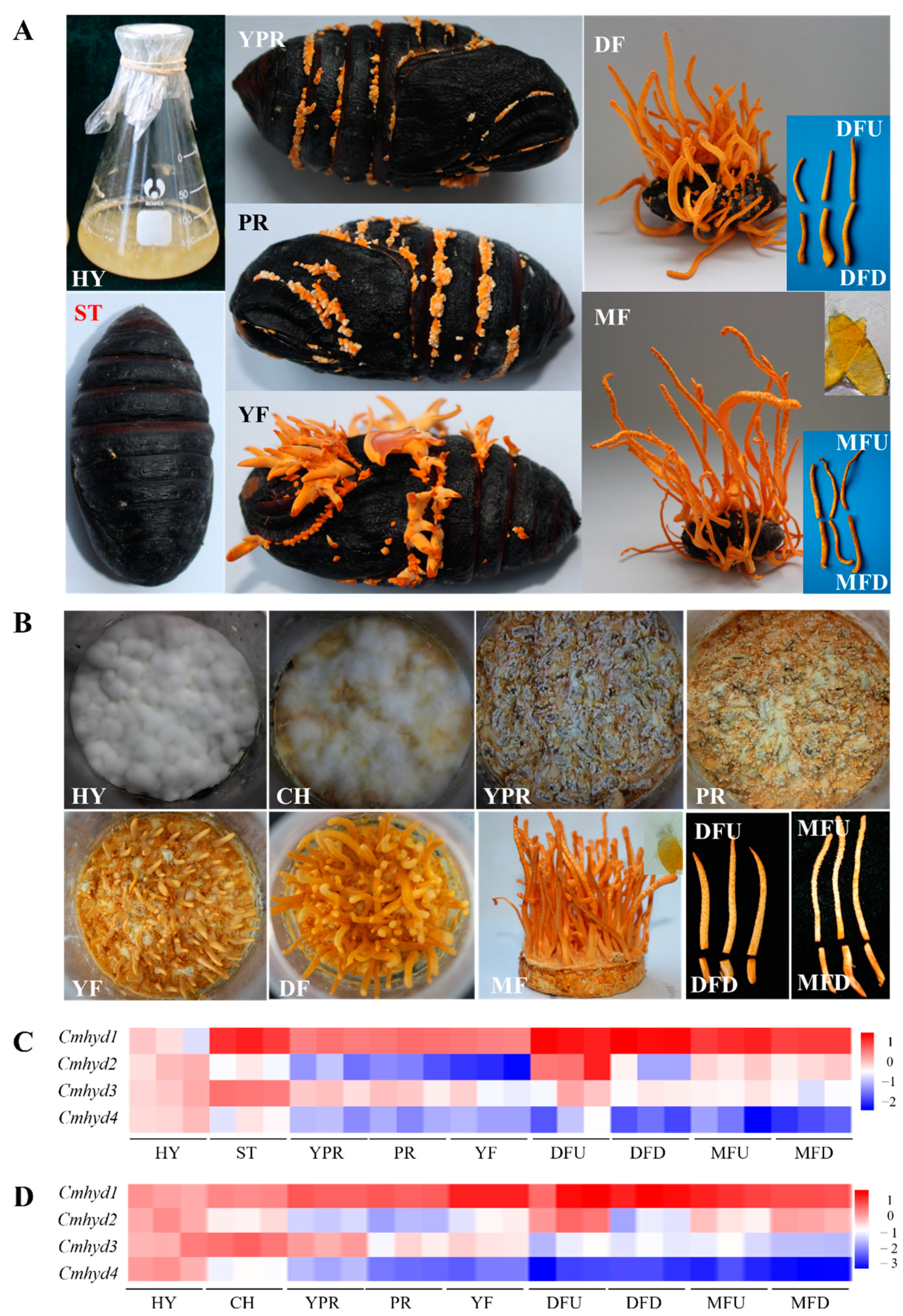
Medicinal mushrooms have become an important component of human culture. The genus Cordyceps is the largest genus in the family Clavicipitaceae, with more than 750 species, and is highly diverse in terms of number of species, morphology, and adaptation to diverse hosts [7, 8]. These diverse species are distributed mainly in humid temperate and tropical habitats in Asian countries (Korea, Japan, Nepal, China, etc.) and other parts of the world. The occurrence of different species in different environmental conditions around the world indicates their global distribution [9,10]. Specific coordinated mechanisms are involved in the relationship between Cordyceps species and their respective hosts. After they evade the immune system and evade the production of protective secondary metabolites by the host, this can be viewed as a promising source of new drugs [9]. Based on this property, these species are gaining importance as a source of natural products with various biological activities [10]. Recently, wild-growing Cordyceps species have been replaced by artificially cultivated specimens because of their rarity and high price associated with collection and processing [11]. C. militaris is an important folk medicinal fungus in traditional Chinese medicine and is widely used in Asia as herbal medicine and functional food [12]. C. militaris is his second most popular and studied species in the genus. Many medicinal benefits of this species have been documented, including glycemic control, lipid-lowering, antitumor, antibacterial, antiviral, antiprotozoan, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, antioxidant, and immunoprotective activities [10, 12]. . Therefore, C. militaryis can be considered an important candidate for the treatment of various diseases. Mycological data for C. militaris are presented below [12]. Natural and cultured C. militaris are shown in Figure 1.
Dried Cordyceps Mushroom
In today's world, the concept of 'prevention is better than cure' prevails, resulting in established food safety and therapeutic profiles. Functional foods can be divided into foods marketed under health food labels and food sources that have physiological properties in addition to their nutritional use. In addition, natural ingredients that can be used regularly or that can affect body systems when consumed are also called functional foods [13, 14].According to the European consensus, the most accurate The definition is that “a food can be considered functional beyond its full nutritional effect if it improves a target function within the body in a way that contributes to improved health and reduced risk of disease”. Functional foods are natural substances. However, various components can be incorporated or removed through biotechnological processes [15] to improve health or prevent disease in individuals or defined groups based on sex and age. [16, 17]. The presence or intentional addition of certain elements such as fiber, flavonoids, polyphenols, anthocyanins, minerals, fatty acids and carotenoids enhance the nutritional value of dietary components. Vitamins, minerals and other nutrients were previously incorporated into functional food formulas. Prebiotics and probiotics that tend to target metabolic syndrome and other diseases [18, 19], hypertension, cell damage and oxidation [18, 20] are well-documented functional foods. They have unique immunomodulatory and immune-enhancing abilities and can enhance immunity through a symbiotic relationship with humans [12]. Apart from therapeutic functions, C. militaris may be a good candidate for consideration as a functional food due to the presence of metabolites with therapeutic or protective functions.
Numerous bioactive components have been identified from this species, including cordycepin, ergosterol, carotenoids, mannitol, proteins, essential amino acids, volatile oils, carotenoids, minerals, vitamins, nucleosides, sterols, and several carbohydrates. It is a monosaccharide, oligosaccharide, and polysaccharide, demonstrating its medical and palliative importance [12]. China's industrial sector is involved in large-scale fermentation and commercial cultivation of interstitium, the reason for the decline of wild populations, to meet the growing demand for medical, food and nutritional purposes [21]. Moreover, the bioactive compounds produced in fermentation cultures are the main reason for its industrial production [21, 22]. Currently, at least 36 health foods made from this medicinal fungus have been approved in China. In addition, C. militaris mycelium health food products in the form of powder (Z20030034) and capsules (Z20030035) have achieved commercially approved partial status, with beneficial effects on the kidneys and lungs, and It is claimed to be effective against cough, asthma and phlegm. , cold hands and feet, fatigue, dizziness, ringing in the ears, and other ailments. Also from Chinese ministries
Cordycep supplement, cordycep, cordycep capsule, cordycep mushroom, cordycep fungi, cordycep mycelium, cordycep flowers, cordycep sinensis, cordycep dxn, cordycep extract, cordycep benefits, cordycep tiens
0 Comments